How to operate a drone safely and effectively is a skill that opens up a world of exciting possibilities, from breathtaking aerial photography to intricate drone racing. This guide provides a step-by-step approach, covering everything from pre-flight checks and basic controls to advanced maneuvers and essential safety procedures. We’ll explore the intricacies of drone components, flight modes, and camera operation, equipping you with the knowledge to confidently take to the skies.
Understanding your drone’s capabilities and limitations is crucial for safe and responsible operation. We’ll delve into the importance of adhering to local regulations and best practices, ensuring that your drone flights are both enjoyable and compliant. Whether you’re a novice pilot or looking to enhance your existing skills, this guide will serve as a valuable resource for your drone journey.
Drone Parts and Components
Understanding the individual components of your drone is crucial for safe and effective operation. This section details the function of each major part and highlights key differences between various types of motors and propellers.
Drone Component Functions, How to operate a drone
A drone’s functionality relies on the coordinated work of several key components. These include propellers, motors, a flight controller, a battery, a GPS module, and a camera.
- Propellers: These generate thrust, propelling the drone through the air. Different propeller designs offer varying levels of thrust and efficiency.
- Motors: These convert electrical energy from the battery into mechanical energy, rotating the propellers. Motor type significantly impacts performance and flight characteristics.
- Flight Controller: The “brain” of the drone, this unit processes data from various sensors and controls the motors to maintain stability and execute flight commands.
- Battery: Provides the power for all drone components. Battery capacity dictates flight time.
- GPS: A Global Positioning System receiver allows for precise positioning and autonomous flight modes, such as Return-to-Home (RTH).
- Camera: Captures images and videos, a key feature for many drone users. Camera quality varies significantly across drone models.
Motor and Propeller Types
Drone motors are typically brushless DC motors, known for their efficiency and reliability. They are categorized by size (measured in KV, which represents the motor’s speed constant), and power output. Propellers are characterized by their diameter and pitch, affecting thrust and speed. Larger diameter propellers generally provide more lift, while a higher pitch results in faster speeds but potentially reduced lift.
Comparison of Popular Drone Models
The following table compares the features of three popular drone models, showcasing the variations in motor types, battery life, and camera resolution. Note that specifications can vary based on the specific model and version.
| Model | Motor Type | Battery Life (approx.) | Camera Resolution |
|---|---|---|---|
| DJI Mavic 3 | Brushless DC | 46 minutes (with standard battery) | 5.1K |
| Autel EVO II Pro | Brushless DC | 40 minutes (with standard battery) | 8K |
| Parrot Anafi USA | Brushless DC | 25 minutes (with standard battery) | 4K HDR |
Pre-Flight Checks and Procedures
A thorough pre-flight checklist is essential for ensuring safe and successful flights. This section Artikels the critical steps to take before each flight, emphasizing the importance of calibration.
Pre-Flight Inspection Checklist
Before each flight, systematically check the following:
- Inspect propellers for damage or wear.
- Verify battery charge level and connection.
- Check all motor functions and responsiveness.
- Confirm GPS signal acquisition and strength.
- Calibrate the compass and IMU (Inertial Measurement Unit).
- Review local airspace regulations and restrictions.
- Ensure the drone is in a safe and open area for takeoff.
Compass and GPS Calibration
Calibrating the compass and GPS before each flight is crucial for accurate positioning and stable flight. An improperly calibrated compass can lead to erratic flight behavior, while a weak GPS signal may result in loss of position awareness. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for proper calibration procedures.
Pre-Flight Procedure Flowchart
A visual representation of the pre-flight procedure can be helpful. A flowchart would typically show a sequence of steps, starting with battery check, progressing through the motor and GPS checks, ending with a final confirmation before takeoff. Each step would have decision points, such as a check for sufficient battery level, a GPS signal check, and a final safety check.
A “No” response at any of these checkpoints would require troubleshooting or postponement of the flight.
Taking Off and Landing
Safe takeoff and landing procedures are fundamental to responsible drone operation. This section details proper techniques and addresses common errors.
Safe Takeoff and Landing Techniques
A smooth and controlled takeoff involves gently increasing throttle until the drone lifts off vertically. Landing should be similarly gradual, reducing throttle smoothly to a gentle descent. Maintain visual contact with the drone throughout the entire process. Avoid sudden movements or abrupt changes in throttle.
Wind Conditions
Wind significantly impacts takeoff and landing. In windy conditions, choose a sheltered location, and orient the drone into the wind to minimize drift during takeoff. For landing, adjust your approach to account for wind direction and speed, ensuring a controlled descent.
Common Takeoff and Landing Errors and Solutions
- Problem: Drone drifting during takeoff. Solution: Increase throttle gradually and compensate for wind. Ensure proper compass calibration.
- Problem: Uncontrolled descent during landing. Solution: Reduce throttle slowly and smoothly. Ensure sufficient battery level.
- Problem: Propeller strike during takeoff or landing. Solution: Choose a clear, level surface. Inspect propellers for damage before each flight.
Basic Flight Controls
Understanding basic flight controls is essential for safe and effective drone operation. This section explains how to control altitude, direction, and speed, and compares different flight modes.
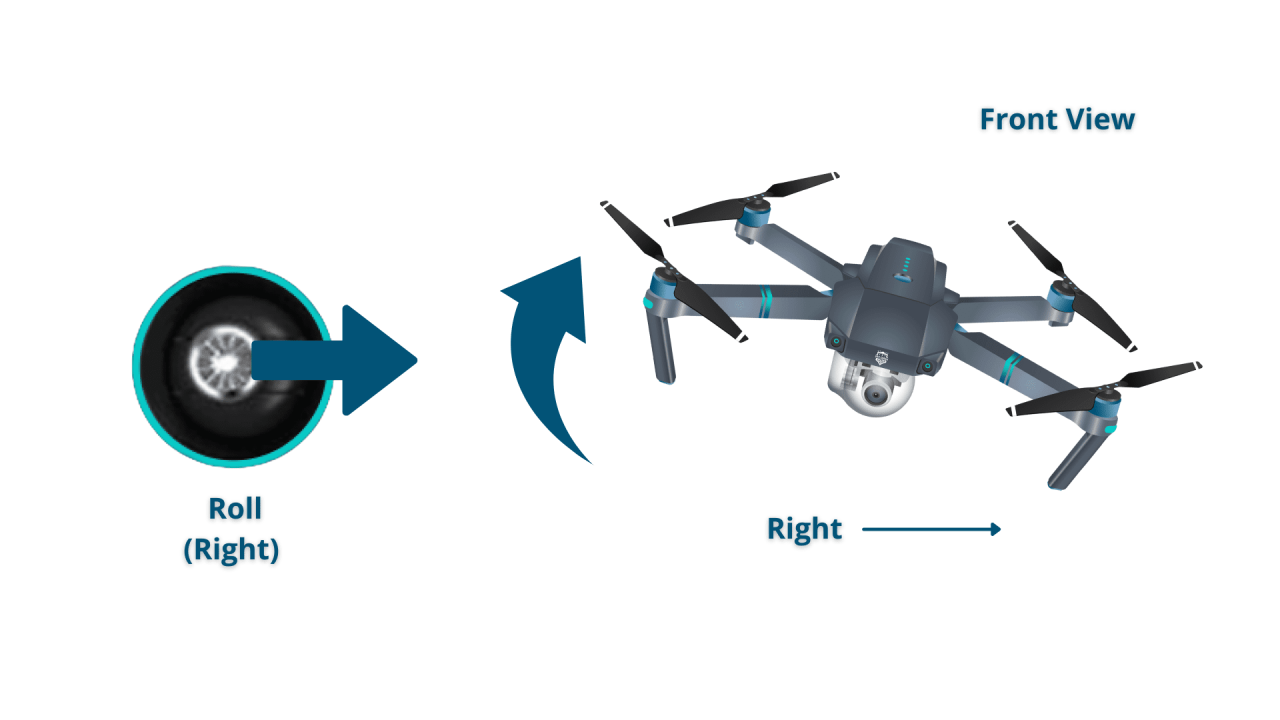
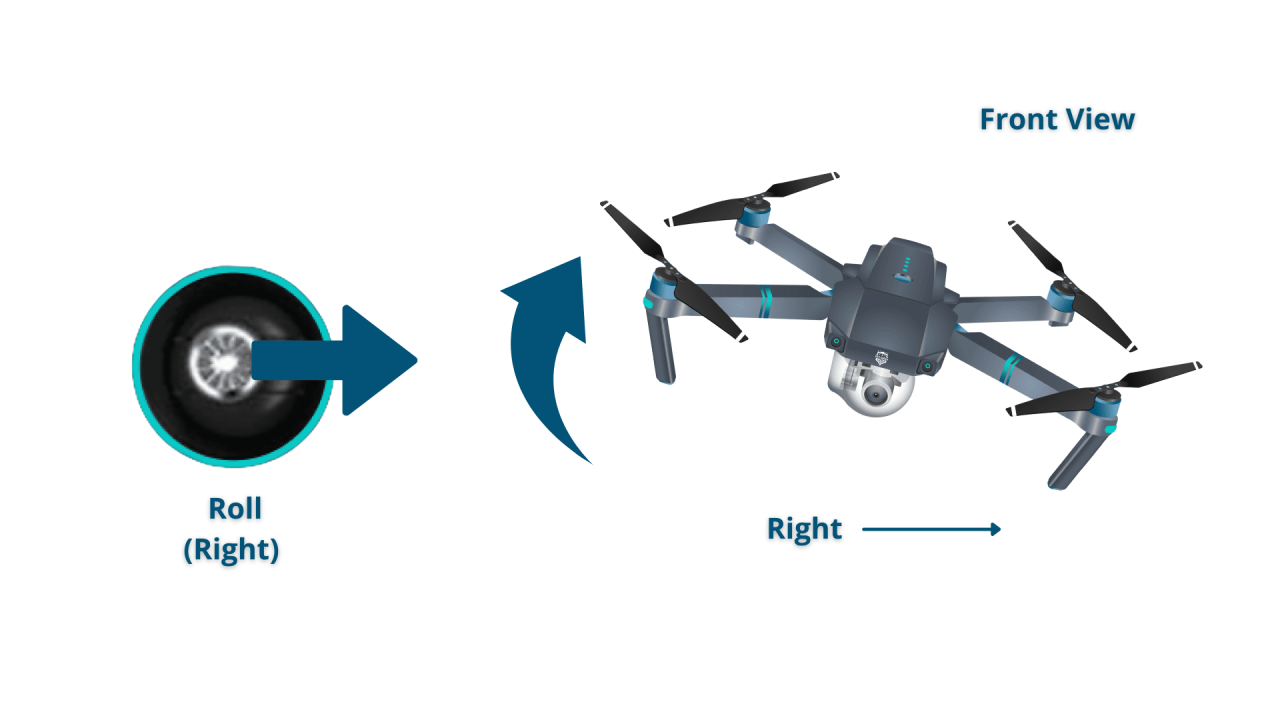
Controlling Altitude, Direction, and Speed
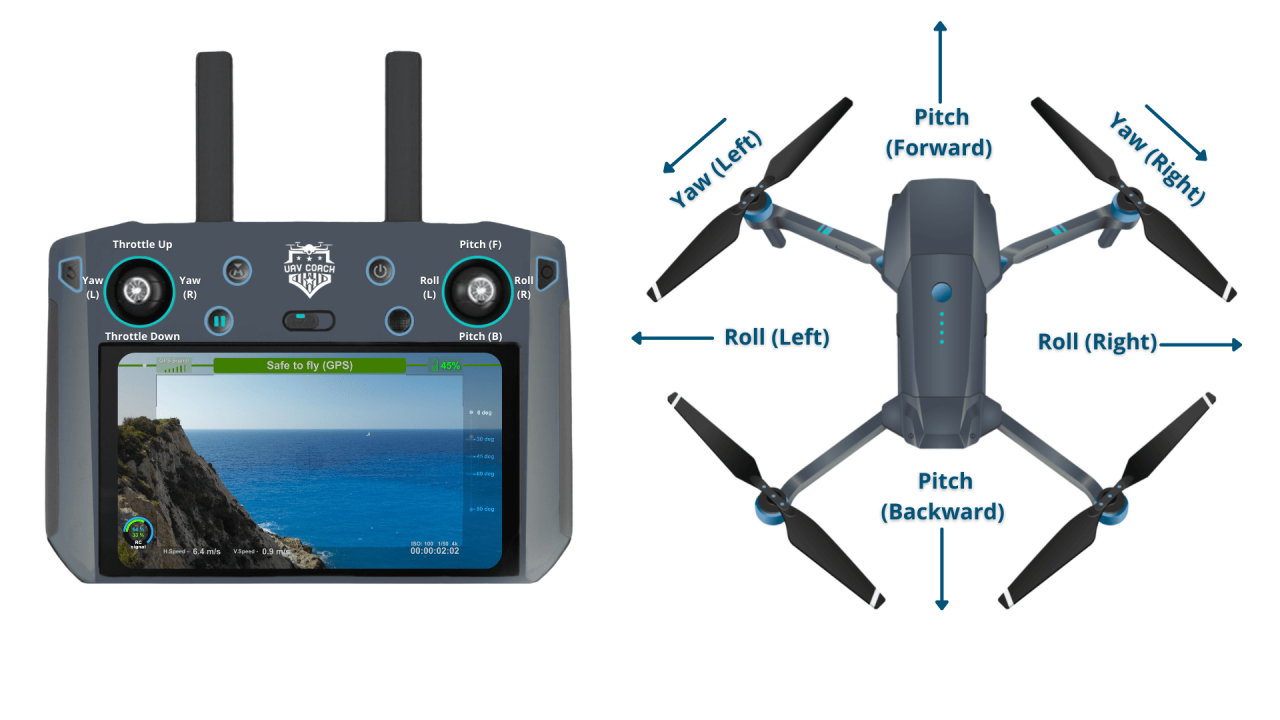

Most drone remote controls use joysticks to control altitude (typically the left stick), direction (left stick, often with a rotational element for yaw), and speed (right stick). Precise control comes with practice and understanding the responsiveness of your specific drone model.
Flight Modes
Different flight modes offer varying levels of control and stability. Beginner modes often limit speed and responsiveness, while expert modes provide full control. GPS mode uses GPS data for position hold and automated functions like Return-to-Home.
Understanding drone operation involves mastering several key skills, from pre-flight checks to navigating airspace regulations. Learning how to handle the controls smoothly is crucial, and a great resource for this is the comprehensive guide on how to operate a drone , which covers everything from basic maneuvers to more advanced techniques. Ultimately, safe and effective drone operation requires consistent practice and a thorough understanding of the technology.
Hazards of Improper Control Input
Improper control inputs can lead to loss of control, collisions, and damage to the drone or its surroundings. Sudden, jerky movements can destabilize the drone, especially in windy conditions. Always maintain a safe distance from obstacles and people.
Understanding drone operation involves mastering several key skills, from pre-flight checks to navigating airspace regulations. Learning the basics is crucial, and a great resource for this is the comprehensive guide on how to operate a drone , which covers everything from takeoff and landing to advanced maneuvers. Successfully operating a drone requires consistent practice and a thorough understanding of safety protocols.
Advanced Flight Maneuvers
This section covers techniques for performing more complex flight maneuvers.
Basic Aerial Maneuvers
Basic maneuvers include hovering (maintaining a fixed position), turns (rotating the drone), ascents (increasing altitude), and descents (decreasing altitude). Mastering these is crucial before attempting more complex maneuvers.
Planning and Executing Complex Flight Paths
Planning complex flight paths requires pre-flight visualization and careful execution. Consider obstacles, wind conditions, and battery life. Many drones offer waypoint programming features to assist with this.
Executing a 360-Degree Rotation
- Maintain a stable hover.
- Use the yaw control (often a dial or rotational movement on the left joystick) to initiate the rotation.
- Slowly and smoothly rotate the drone 360 degrees.
- Maintain a constant altitude and avoid abrupt movements.
- Return to a stable hover once the rotation is complete.
Drone Camera Operation
This section focuses on effectively utilizing your drone’s camera capabilities.
Camera Settings and Image Quality
Camera settings such as ISO, shutter speed, aperture (if adjustable), and white balance significantly impact image quality. Experiment to find optimal settings for various lighting conditions. Higher ISO values are better for low-light conditions but may introduce noise. Faster shutter speeds freeze motion, while slower speeds can create motion blur.
Capturing High-Quality Photos and Videos
- Choose the appropriate camera mode (photo or video).
- Adjust settings based on lighting and desired effect.
- Compose your shot carefully, considering framing and perspective.
- Maintain a steady flight for smooth video.
- Use the drone’s features for stabilization (like electronic image stabilization).
Proper Framing and Composition
Effective aerial photography involves careful consideration of framing and composition. The “rule of thirds” is a useful guideline, placing key elements off-center for a more visually appealing image. Experiment with different angles and perspectives to capture unique shots.
Battery Management and Charging
Proper battery management is crucial for maximizing flight time and ensuring the safety and longevity of your drone’s battery.
Maximizing Battery Life and Performance
- Avoid extreme temperatures during operation and storage.
- Store batteries at a partially charged state (around 30-50%).
- Avoid completely discharging batteries.
- Use the manufacturer-recommended charger.
Safety Precautions When Charging
Always use the manufacturer-recommended charger and follow its instructions carefully. Never leave batteries unattended while charging. Ensure proper ventilation to prevent overheating. Use a fire-resistant surface when charging.
Proper Storage and Maintenance
Store batteries in a cool, dry place away from flammable materials. Regularly check for any signs of damage or swelling. Dispose of damaged batteries properly according to local regulations.
Drone Maintenance and Troubleshooting: How To Operate A Drone
Regular maintenance and troubleshooting skills are essential for keeping your drone in optimal condition.
Comprehensive Maintenance Schedule
A regular maintenance schedule should include inspections of propellers, motors, and the flight controller. Check for loose screws, damaged parts, and signs of wear and tear. Clean the drone after each flight to remove dirt and debris.
Common Drone Malfunctions and Causes
- Problem: Drone not responding to controls. Possible Causes: Low battery, faulty connection, software glitch.
- Problem: GPS signal loss. Possible Causes: Obstructions, weak signal, interference.
- Problem: Motor failure. Possible Causes: Overheating, damage, faulty ESC (Electronic Speed Controller).
Troubleshooting Guide
A troubleshooting guide would systematically address common problems, starting with simple checks (like battery level and power connections) and progressing to more complex issues (like motor replacement or firmware updates). Consult your drone’s manual for specific troubleshooting steps.
Safety Regulations and Best Practices
Understanding and adhering to safety regulations and best practices is crucial for responsible drone operation.
Legal Requirements for Drone Operation
Drone regulations vary by location. Research and understand the specific rules and regulations in your area before flying. This typically includes registration requirements, airspace restrictions, and limitations on flight time and distance.
Respecting Airspace Regulations

Avoid flying near airports, heliports, and other restricted airspace. Be aware of no-fly zones and adhere to all airspace regulations. Utilize online resources to check airspace restrictions before each flight.
Best Practices for Safe Drone Operation
- Always maintain visual line of sight with your drone.
- Avoid flying in adverse weather conditions (strong winds, rain, snow).
- Never fly over crowds or people.
- Respect privacy and avoid flying over private property without permission.
Emergency Procedures
Knowing how to handle emergencies is a critical aspect of responsible drone piloting.
Loss of Control or Emergency Situations
In case of loss of control, immediately attempt to regain control using the emergency controls provided by your drone’s system. If unable to regain control, prioritize a safe landing procedure. This might involve selecting the Return-to-Home (RTH) function if available.
Emergency Landing
An emergency landing should prioritize safety and minimize potential damage. Choose a clear, open area, and gradually reduce throttle to effect a controlled descent. If necessary, prepare for impact by attempting to land in soft terrain.
Recovering a Crashed Drone
Carefully inspect the drone for damage after a crash. Repair or replace damaged components as needed. If the damage is extensive, consider contacting the manufacturer or a qualified repair service.
Mastering the art of drone operation is a rewarding experience that combines technical skill with creative expression. By following the guidelines Artikeld in this guide, you’ll be well-equipped to handle your drone with confidence and safety. Remember that consistent practice, adherence to regulations, and a respect for the airspace around you are key to becoming a proficient and responsible drone pilot.
Soar responsibly and enjoy the incredible perspective that drone flight offers!
FAQ Corner
What is the best type of drone for beginners?
Many user-friendly drones with GPS stabilization and beginner modes are ideal for beginners. Look for models with features like automatic takeoff/landing and return-to-home functionality.
How far can I fly my drone?
The maximum distance depends on the drone model and local regulations. Always stay within visual line of sight and check for any airspace restrictions.
What should I do if my drone loses connection?
Most drones have a “return-to-home” function. If that fails, attempt to regain control manually. If unsuccessful, prioritize safety and let the drone land itself or gently guide it to a safe landing zone.
How often should I calibrate my drone’s compass?
It’s recommended to calibrate your drone’s compass before each flight, especially if you’re flying in areas with strong magnetic interference.